U.S. plant-based meat sales growth accelerates despite Covid-19

The Covid-19 pandemic has had a dramatic effect on all sectors of the economy, and the food industry is no exception. The early weeks of nationwide shutdowns led to long lines and empty shelves at retail locations, and foodservice operations ground to a halt as restaurants were forced to close. Despite these challenges, several plant-based categories have experienced strong retail sales growth in the United States during the crisis.
Plant-based meat sales continue to grow.
Plant-based meat in particular has performed well over the past few months. IRI retail sales data from The Analogue Dish shows that plant-based meat dollar and volume sales experienced strong growth—double to triple digits—compared to the same weeks in 2019. Both dollar and volume sales of plant-based meat experienced an especially high bump in March due to pantry stocking.
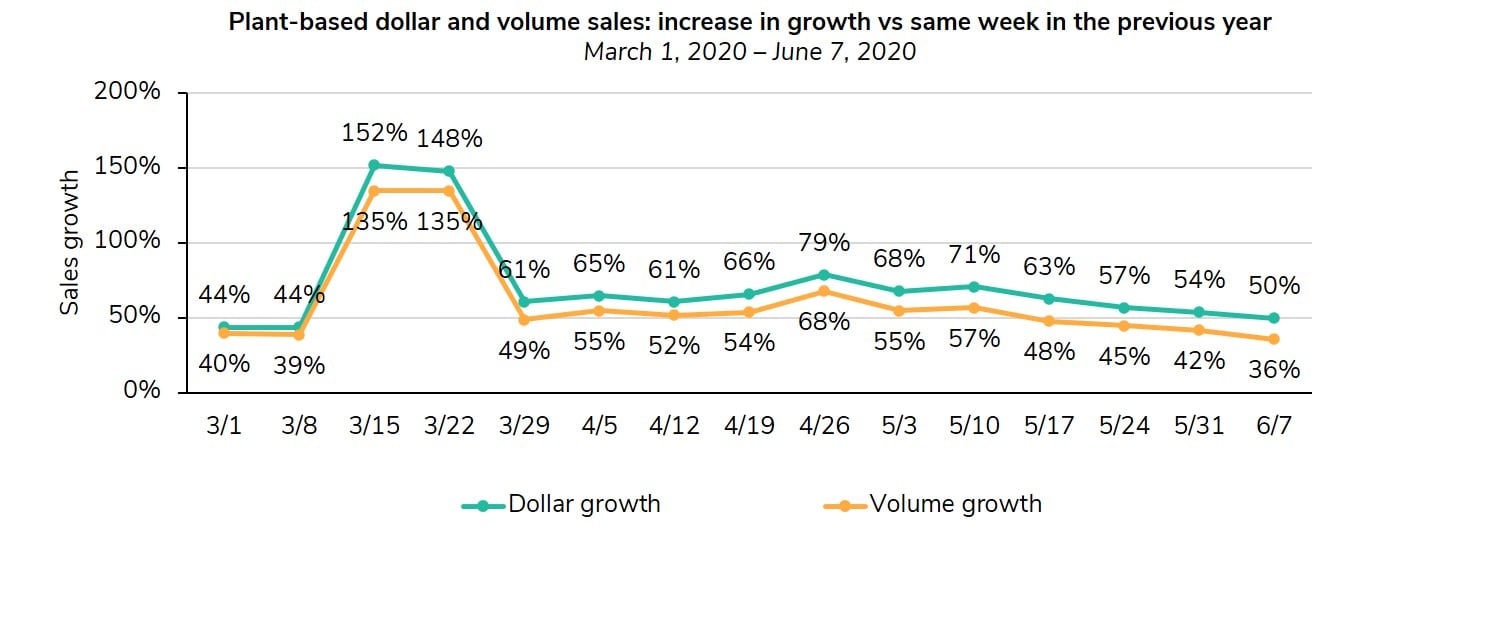
Plant-based meat dollar sales growth has not only outperformed its prior-year performance, but it has also outperformed animal-based meat’s dollar sales growth over the same time period. Plant-based meat’s dollar sales growth continued to outperform animal-based meat’s dollar sales growth through April and into May.

Fresh plant-based meat—increasingly sold in the meat aisle alongside conventional animal meat—has done particularly well during this period, experiencing growth as high as 454 percent versus the same week in 2019 during the pantry stocking bump. During the same time period, fresh animal-based meat experienced a sales growth high of 100 percent, with week-by-week growth much lower over the course of April, May, and June.

This sales data indicates there is growing consumer interest in plant-based meat. Despite the unprecedented societal disruption and economic uncertainty brought about by Covid-19, consumers are still purchasing plant-based meat, and the category’s sales growth is higher than both its own past performance and animal-based meat’s current growth.
Covid-19 highlights benefits of the plant-based meat supply chain.
The first few months of the Covid-19 pandemic revealed the inherent insecurity of the animal-based meat supply chain. The animal-based meat supply chain is long with many points of failure. Animals must be raised, slaughtered, processed, packaged, and distributed, and shutdowns at slaughterhouses due to outbreaks of Covid-19 quickly led to disruptions along this supply chain. Retailers like Costco and Kroger, as well as restaurants like Wendy’s, began rationing sales of meat and burgers in response to the slowdown in meat production.
By removing animals from the production equation, plant-based meat companies are not beholden to the systemic shocks affecting the animal-based meat supply chain. While the animal-based meat supply chain was experiencing significant disruption, Impossible Foods expanded into 777 more grocery stores around the country. Less than a month later, Impossible Foods launched the Impossible Burger into 1,700 Kroger stores nationwide.
Consumer perceptions of plant-based meat are shifting amid the pandemic.
The Covid-19 pandemic has also had an effect on consumer perceptions of animal-based and plant-based meat. A Datassential study asked consumers how knowledge that workers at meat plants in the United States have been diagnosed with Covid-19 would affect their purchasing. 25 percent of respondents indicated they would be less likely to buy animal-based meat from retail, and 29 percent reported they would be less likely to order animal-based meat dishes from restaurants. When these responses are cut by generation, Gen Z and Millennials report that they are less likely to purchase or order animal-based meat at higher percentages than the total sample of consumers.


The same Datassential study found that 47 percent of U.S. consumers are willing to switch to eating more plant-based meat in the event Covid-19 leads to meat shortages. Gen Z and Millennials are more likely to switch to eating more plant-based meat, at 62 percent and 56 percent, respectively. When presented with a scenario in which there were no beef burgers available at a restaurant, 12 percent of consumers reported that they would order a plant-based burger.
Covid-19 is also influencing consumer behavior.
In addition to shifting consumer perceptions, Covid-19 is, in fact, influencing consumer behavior. As noted by Mintel in its recent Plant-Based Proteins 2020 report, 48 percent of U.S. consumers have increased the amount of shopping done online as a result of Covid-19. Direct-to-consumer offerings of plant-based meat will keep these products accessible as more and more consumers shift to e-commerce to avoid shopping in physical stores. Plant-based meat companies like Impossible Foods and The Meatless Farm Co. have already begun selling their products to consumers through their own websites, and other plant-based brands will likely follow suit.
With regards to long term shifts in consumer behavior, a report by the University of Missouri’s Food & Agricultural Policy Research Institute predicts that U.S. animal-based meat consumption will decline due to increasing retail prices and decreasing consumer disposable income. Bloomberg reports that this would be the first decline in U.S. animal-based meat consumption since 2014. This potential drop in animal-based meat consumption opens up the door for plant-based meat products to take an increasingly larger share of the total meat market.
The data is clear: The plant-based meat category has remained resilient in the face of economic uncertainty, outperforming both its prior-year growth rates and animal-based meat’s growth rates. While animal-based meat experienced supply chain disruptions, plant-based meat emerged unscathed. Covid-19 will likely have long-lasting effects on the U.S. and global food industries and will influence consumer preferences. It is in companies’ best interests to embrace the growth and security that plant-based meat provides.
Want more insights about the latest developments in the alternative protein industry? Check out GFI’s State of the Industry Reports, and visit GFI’s Investor Resources webpage for further resources.

